A Summarized History of the Geodesic Dome
The first known dome was created circa 100 AD, when the Romans created the first monolithic dome by rotating an arch 360°. In a monolithic dome, the forces push inward towards the center peak of the dome
Because these domes were so exceptionally heavy to build with masonry materials, designers took to carving out arches sitting on top of one another within the dome structure, in order to lessen the weight.
The Mihrimah Mosque, completed in 1555 by the architect Sinan, has 161 arched windows.
Architects continued to try new techniques to make their domes lighter, stronger, and more material-efficient.
In the early 1400's, engineers in Rome came up with the technique of covering a strong inner dome with a higher, weaker outer dome, in order to create domes with a higher peak. The US Capitol is built in such a manner, with a strong iself-supporting dome on the inside and a thin shell for the outer dome, supported by iron ribs.

In the 1700's, St. Peter's Basilica began to crack. In hopes of saving the dome from collapse, Vatican engineers placed iron rings, dubbed tension rings, around the dome. These rings succeeded in rechanneling the stress on the dome structure so that it pushed inward to the center rather than outward to the base.
The geodesic dome was invented in the 1950's by American
Buckminster Fuller, an engineer and architect. Instead of using arches,
this new dome design was created out of a series of triangles. When forced
is placed on the structure, all of the triangles within it push with equal force
in every direction. In this way, the design redistributes the stress so
that the structure is much stronger than that of an arch.
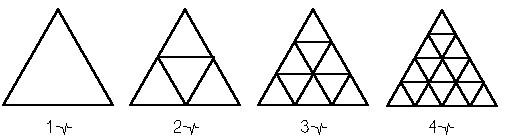
The frequency of a dome is the number of triangles per specific area. A dome with a higher frequency has more triangles per given space than a lower-frequency dome. As a result, higher-frequency domes follow more of a spherical shape.
one-frequency dome: two-frequency dome:


Also, domes with even-numbered frequencies are cleanly divisible into hemispheres, so they lie flat:

